- Home
-
Help
How to Use
Here is your chance to explore how fluids flow in whatever way you want. There are 5 sections that will help you learn about how fluids move through a pipeline.
The Basics
Want to know more about flow? Head to the basics section and get the scoop on pressure.
Experiment
Here is your chance to experiment and move fluids for yourself. Try out different methods to control the flow of fluids.
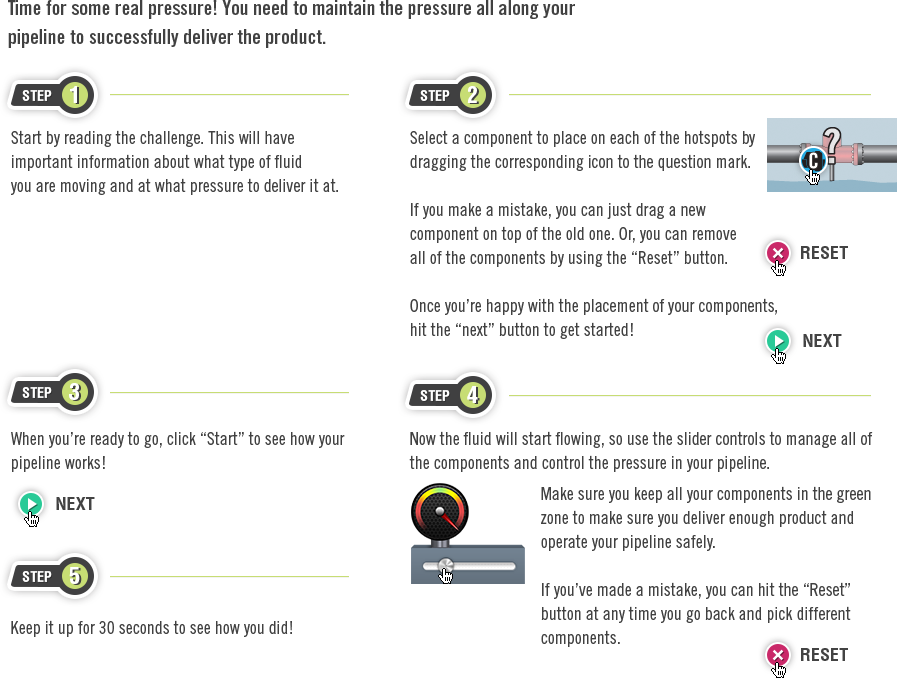
Challenge
Now it's time to apply all your knowledge. Complete the challenge and see how you stack up.
Test Yourself
Think you know it all? Test yourself to see if you are the real deal! You have three questions to answer, but if you're feeling brave you can add some more.
If you're ever unsure of what a word means, check out the definition in the glossary! You can also click on any highlighted word to take you straight there.
-
Teacher Info
Overview
Pipeline Pressure provides students an opportunity to explore a science topic in their own way, at their own pace.
The four sections of the tool have been designed to guide students through the process of understanding fluid flow and pipeline pressure, and let them put that information into practice. Students will gain knowledge of the topic by reading the basics, experimenting without consequence to learn the techniques, applying their knowledge to solve a challenge, and assessing their knowledge with a self-test. A comprehensive glossary also lets them check definitions at any time along the way.
This tool provides a way to teach the elements of the science unit, but also puts science into perspective with real world examples, challenges students to use technology to further their understanding of science, and engages them with a wide range of activities.Curriculum
Grade 8 – Mix and Flow of Matter
SLE #4 - Identify, interpret and apply technologies based on properties of fluids.
-
Glossary
- Compressible
- The measure of the relative volume change of a fluid or solid in response to pressure.
- Compressor
- Compressors are used to increase the pressure of gases, such as natural gas. These pressure differences are required to move gases through their containers. In pipelines, compressor stations are strategically placed along the length of the pipeline to maintain required flow rates.
- Fluids
- A substance that has no fixed shape and yields easily to external pressure. Gases and liquids are examples of fluids.
- Force
- A force is anything that causes an object to undergo a certain change concerning its movement, direction, or geometrical construction.
- Friction
- The resistance that a moving object encounters when in contact with another object.
- Gravity
- The force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth, or toward any other physical body having mass.
- Incompressible
- Incapable of or resistant to compression.
- Pipeline Control Centre Operator
- Pipeline Control Centre Operators monitor and manage pipeline activities for large regions from one centralized control centre. They monitor flow, product quality, and line balance, and manage them by operating control valves, compressors, and pumps remotely.
- Pressure
- Pressure is the force exerted on a given area expressed in Pascals (Pa) or in pounds per square inch (PSI). In pipelines, oil and natural gas transported within a pipeline exert pressure on the pipe walls.
- Pump
- A pump is a mechanical device used to increase the pressure of a liquid in a container, such as oil in a pipeline. This increased pressure is used to push the liquid through the container towards an area of lower pressure.
- SCADA
- SCADA is a pipeline control system. It gathers information from the pipelines and transmits it to a control facility where the data can be monitored and analyzed. The operator can then issue commands to remote sites to perform actions like opening and closing valves, or starting and stopping pumps or compressors.
- Valve
- A valve is a mechanical device installed in a pipeline and opened or closed to control the flow of fluids. They are most often placed where they can close to stop the flow of fluid, and allow sections of the pipelines to be separated for repair. Some valves are also used to control the pressure and/or flow rates in pipelines.
- Credits
Your overall score
Read each slide to earn maximum points.
Explore the simulator. Try out all the different combinations to earn maximum points.
Successfully complete all 5 levels to earn maximum points.
Earn 5 points for every question correctly answered.